You are given a 0-indexed integer array arr, and an m x n integer matrix mat. arr and mat both contain all the integers in the range [1, m * n].
Go through each index i in arr starting from index 0 and paint the cell in mat containing the integer arr[i].
Return the smallest index i at which either a row or a column will be completely painted in mat.
Example 1:
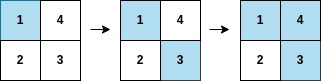
Input: arr = [1,3,4,2], mat = [[1,4],[2,3]] Output: 2 Explanation: The moves are shown in order, and both the first row and second column of the matrix become fully painted at arr[2].
Example 2:
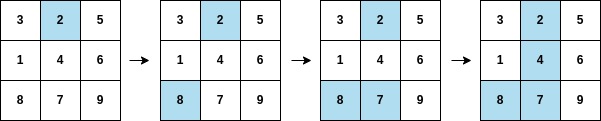
Input: arr = [2,8,7,4,1,3,5,6,9], mat = [[3,2,5],[1,4,6],[8,7,9]] Output: 3 Explanation: The second column becomes fully painted at arr[3].
Constraints:
m == mat.lengthn = mat[i].lengtharr.length == m * n1 <= m, n <= 1051 <= m * n <= 1051 <= arr[i], mat[r][c] <= m * n- All the integers of
arrare unique. - All the integers of
matare unique.
Approach 01:
-
C++
-
Python
class Solution {
public:
int firstCompleteIndex(vector<int>& paintOrder, vector<vector<int>>& matrix) {
const int numRows = matrix.size();
const int numCols = matrix[0].size();
// paintedRows[i]: the count of painted cells in the i-th row
vector<int> paintedRows(numRows);
// paintedCols[j]: the count of painted cells in the j-th column
vector<int> paintedCols(numCols);
// cellToRow[cellValue]: the row index of cellValue in the matrix
vector<int> cellToRow(numRows * numCols + 1);
// cellToCol[cellValue]: the column index of cellValue in the matrix
vector<int> cellToCol(numRows * numCols + 1);
// Map each cell value to its corresponding row and column in the matrix
for (int row = 0; row < numRows; ++row) {
for (int col = 0; col < numCols; ++col) {
cellToRow[matrix[row][col]] = row;
cellToCol[matrix[row][col]] = col;
}
}
// Process the painting order and track row/column completion
for (int index = 0; index < paintOrder.size(); ++index) {
int row = cellToRow[paintOrder[index]];
int col = cellToCol[paintOrder[index]];
if (++paintedRows[row] ==
numCols) // Check if the row is completely painted
return index;
if (++paintedCols[col] ==
numRows) // Check if the column is completely painted
return index;
}
throw; // This should not happen as the problem guarantees a valid solution
}
};
class Solution:
def firstCompleteIndex(self, paintOrder: list[int], matrix: list[list[int]]) -> int:
numRows = len(matrix)
numCols = len(matrix[0])
# paintedRows[i]: the count of painted cells in the i-th row
paintedRows = [0] * numRows
# paintedCols[j]: the count of painted cells in the j-th column
paintedCols = [0] * numCols
# cellToRow[cellValue]: the row index of cellValue in the matrix
cellToRow = [0] * (numRows * numCols + 1)
# cellToCol[cellValue]: the column index of cellValue in the matrix
cellToCol = [0] * (numRows * numCols + 1)
# Map each cell value to its corresponding row and column in the matrix
for row in range(numRows):
for col in range(numCols):
cellToRow[matrix[row][col]] = row
cellToCol[matrix[row][col]] = col
# Process the painting order and track row/column completion
for index, cellValue in enumerate(paintOrder):
row = cellToRow[cellValue]
col = cellToCol[cellValue]
paintedRows[row] += 1 # Increment the count for the row
paintedCols[col] += 1 # Increment the count for the column
if paintedRows[row] == numCols: # Check if the row is completely painted
return index
if paintedCols[col] == numRows: # Check if the column is completely painted
return index
raise RuntimeError("A valid solution is guaranteed, this should not occur.")
Time Complexity:
- Mapping Matrix Cells:
To map each cell value in the matrix to its corresponding row and column, we traverse the entire matrix. This takes \( O(m \times n) \), where \( m \) is the number of rows and \( n \) is the number of columns.
- Processing the Painting Order:
We iterate through the painting order, which has a length of \( p \), and for each cell, we perform constant-time operations such as updating counters and checking completion conditions. This takes \( O(p) \).
- Overall Time Complexity:
The total time complexity is \( O(m \times n + p) \), where \( p \) is the size of the painting order.
Space Complexity:
- Auxiliary Space:
We use:
- A vector
paintedRowsof size \( m \). - A vector
paintedColsof size \( n \). - Two vectors
cellToRowandcellToColof size \( m \times n + 1 \).
- A vector
- Overall Space Complexity:
The total space complexity is \( O(m \times n) \).