Given an m x n integer matrix heightMap representing the height of each unit cell in a 2D elevation map, return the volume of water it can trap after raining.
Example 1:
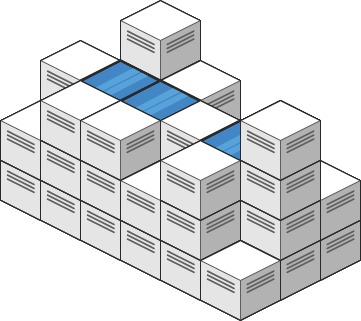
Input: heightMap = [[1,4,3,1,3,2],[3,2,1,3,2,4],[2,3,3,2,3,1]] Output: 4 Explanation: After the rain, water is trapped between the blocks. We have two small ponds 1 and 3 units trapped. The total volume of water trapped is 4.
Example 2:
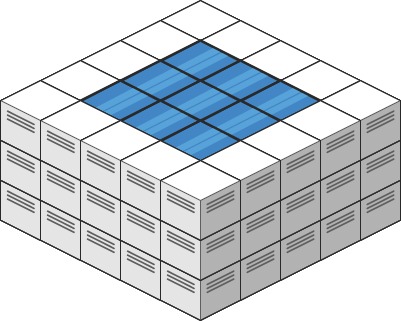
Input: heightMap = [[3,3,3,3,3],[3,2,2,2,3],[3,2,1,2,3],[3,2,2,2,3],[3,3,3,3,3]] Output: 10
Constraints:
m == heightMap.lengthn == heightMap[i].length1 <= m, n <= 2000 <= heightMap[i][j] <= 2 * 104
Approach 01:
-
C++
-
Python
struct Cell {
int row;
int col;
int height; // heightMap[row][col] or the height after filling water
};
class Solution {
public:
int trapRainWater(vector<vector<int>>& heightMap) {
constexpr int directions[4][2] = {{0, 1}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {-1, 0}};
const int rows = heightMap.size();
const int cols = heightMap[0].size();
int totalWater = 0;
auto compare = [](const Cell& a, const Cell& b) { return a.height > b.height; };
priority_queue<Cell, vector<Cell>, decltype(compare)> minHeap(compare);
vector<vector<bool>> visited(rows, vector<bool>(cols, false));
// Push boundary cells into the min-heap and mark them as visited
for (int i = 0; i < rows; ++i) {
minHeap.emplace(Cell{i, 0, heightMap[i][0]});
minHeap.emplace(Cell{i, cols - 1, heightMap[i][cols - 1]});
visited[i][0] = true;
visited[i][cols - 1] = true;
}
for (int j = 1; j < cols - 1; ++j) {
minHeap.emplace(Cell{0, j, heightMap[0][j]});
minHeap.emplace(Cell{rows - 1, j, heightMap[rows - 1][j]});
visited[0][j] = true;
visited[rows - 1][j] = true;
}
// Process the heap
while (!minHeap.empty()) {
const auto [row, col, height] = minHeap.top();
minHeap.pop();
for (const auto& [dx, dy] : directions) {
const int newRow = row + dx;
const int newCol = col + dy;
if (newRow < 0 || newRow >= rows || newCol < 0 || newCol >= cols)
continue;
if (visited[newRow][newCol])
continue;
if (heightMap[newRow][newCol] < height) {
totalWater += height - heightMap[newRow][newCol]; // Water trapped
minHeap.emplace(Cell{newRow, newCol, height}); // Update height
} else {
minHeap.emplace(Cell{newRow, newCol, heightMap[newRow][newCol]});
}
visited[newRow][newCol] = true;
}
}
return totalWater;
}
};
import heapq
class Solution:
def trapRainWater(self, heightMap: list[list[int]]) -> int:
directions = [(0, 1), (1, 0), (0, -1), (-1, 0)]
rows = len(heightMap)
cols = len(heightMap[0])
totalWater = 0
minHeap = []
visited = [[False] * cols for _ in range(rows)]
# Push boundary cells into the min-heap and mark them as visited
for i in range(rows):
heapq.heappush(minHeap, (heightMap[i][0], i, 0))
heapq.heappush(minHeap, (heightMap[i][cols - 1], i, cols - 1))
visited[i][0] = True
visited[i][cols - 1] = True
for j in range(1, cols - 1):
heapq.heappush(minHeap, (heightMap[0][j], 0, j))
heapq.heappush(minHeap, (heightMap[rows - 1][j], rows - 1, j))
visited[0][j] = True
visited[rows - 1][j] = True
# Process the heap
while minHeap:
height, row, col = heapq.heappop(minHeap)
for dx, dy in directions:
newRow, newCol = row + dx, col + dy
if newRow < 0 or newRow >= rows or newCol < 0 or newCol >= cols:
continue
if visited[newRow][newCol]:
continue
if heightMap[newRow][newCol] < height:
totalWater += height - heightMap[newRow][newCol] # Water trapped
heapq.heappush(minHeap, (height, newRow, newCol)) # Update height
else:
heapq.heappush(minHeap, (heightMap[newRow][newCol], newRow, newCol))
visited[newRow][newCol] = True
return totalWater
Time Complexity:
- Heap Operations:
Each cell in the grid is pushed into or popped from the heap exactly once. The heap operations (push and pop) take \( O(\log(r \cdot c)) \), where \( r \) and \( c \) are the number of rows and columns, respectively.
- Neighbor Exploration:
For each cell, the algorithm explores its four neighbors, leading to \( O(4 \cdot r \cdot c) = O(r \cdot c) \) operations.
- Overall Time Complexity:
The total time complexity is \( O((r \cdot c) \cdot \log(r \cdot c)) \).
Space Complexity:
- Heap Storage:
The heap can store up to \( r \cdot c \) cells, requiring \( O(r \cdot c) \) space.
- Visited Matrix:
The visited matrix requires \( O(r \cdot c) \) space to track processed cells.
- Overall Space Complexity:
The overall space complexity is \( O(r \cdot c) \).