You are given a 0-indexed 1-dimensional (1D) integer array original, and two integers, m and n. You are tasked with creating a 2-dimensional (2D) array with m rows and n columns using all the elements from original.
The elements from indices 0 to n - 1 (inclusive) of original should form the first row of the constructed 2D array, the elements from indices n to 2 * n - 1 (inclusive) should form the second row of the constructed 2D array, and so on.
Return an m x n 2D array constructed according to the above procedure, or an empty 2D array if it is impossible.
Example 1:
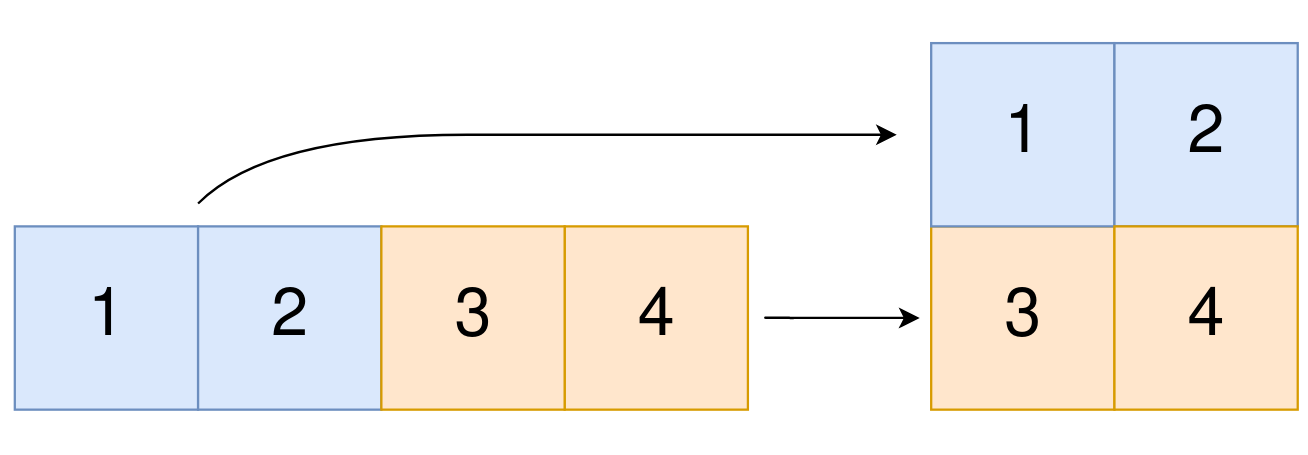
Input: original = [1,2,3,4], m = 2, n = 2 Output: [[1,2],[3,4]] Explanation: The constructed 2D array should contain 2 rows and 2 columns. The first group of n=2 elements in original, [1,2], becomes the first row in the constructed 2D array. The second group of n=2 elements in original, [3,4], becomes the second row in the constructed 2D array.
Example 2:
Input: original = [1,2,3], m = 1, n = 3 Output: [[1,2,3]] Explanation: The constructed 2D array should contain 1 row and 3 columns. Put all three elements in original into the first row of the constructed 2D array.
Example 3:
Input: original = [1,2], m = 1, n = 1 Output: [] Explanation: There are 2 elements in original. It is impossible to fit 2 elements in a 1x1 2D array, so return an empty 2D array.
Constraints:
1 <= original.length <= 5 * 1041 <= original[i] <= 1051 <= m, n <= 4 * 104
Approach 01:
-
C++
-
Python
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> construct2DArray(vector<int>& original, int m, int n) {
vector<vector<int>> result;
// Check if the size of the original array matches the 2D array dimensions
if (original.size() != m * n) {
return {}; // Return an empty array if the sizes do not match
}
// Construct the 2D array
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
vector<int> row(original.begin() + (i * n), original.begin() + (i + 1) * n);
result.push_back(row);
}
return result;
}
};
class Solution:
def construct2DArray(self, original: List[int], m: int, n: int) -> List[List[int]]:
result = []
if(len(original) != (m*n)):
return []
for i in range(m):
result.append(original[(i*n):(i+1)*n])
return result
Time Complexity
- Checking the Size:
Verifying if the size of the original array matches the required size of the 2D array is an \( O(1) \) operation.
- Constructing the 2D Array:
The solution uses a loop to create the 2D array from the original 1D array. This loop runs
mtimes, and for each iteration, a subarray of sizenis constructed usingoriginal.begin() + (i * n)andoriginal.begin() + (i + 1) * n. Constructing each subarray takes \( O(n) \) time, making the total time complexity \( O(m \cdot n) \). - Overall Time Complexity:
The overall time complexity is \( O(m \cdot n) \), where
mis the number of rows andnis the number of columns in the 2D array.
Space Complexity
- Space for Result:
The solution uses an additional vector of vectors (
result) to store the constructed 2D array. The space required for this result is \( O(m \cdot n) \) because it needs to store all the elements of the original array in a 2D format. - Overall Space Complexity:
The overall space complexity is \( O(m \cdot n) \), primarily due to the space required to store the result.