Given elements as nodes of the two singly linked lists. The task is to multiply these two linked lists, say L1 and L2.
Note: The output could be large take modulo 109+7.
Examples :
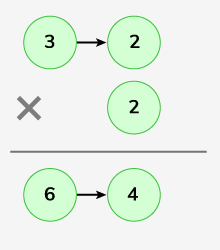
Input: LinkedList L1 : 3->2 , LinkedList L2 : 2
Output: 64 Explanation:
Multiplication of 32 and 2 gives 64.
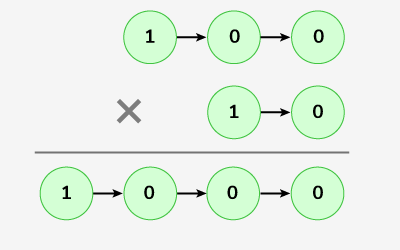
Input: LinkedList L1: 1->0->0 , LinkedList L2 : 1->0
Output: 1000 Explanation:
Multiplication of 100 and 10 gives 1000.
Expected Time Complexity: O(max(n,m))
Expected Auxilliary Space: O(1)
where n is the size of L1 and m is the size of L2
Constraints:
1 <= number of nodes <= 9
0 <= node->data <= 9
Approach 01:
-
C++
-
Python
class solution {
public:
long long multiplyTwoLists(Node* firstList, Node* secondList) {
Node* currentNode = firstList;
std::string firstNumberString;
while (currentNode != nullptr) {
int digit = currentNode->data;
firstNumberString += std::to_string(digit);
currentNode = currentNode->next;
}
long long firstNumber = std::stoll(firstNumberString);
currentNode = secondList;
std::string secondNumberString;
while (currentNode != nullptr) {
int digit = currentNode->data;
secondNumberString += std::to_string(digit);
currentNode = currentNode->next;
}
long long secondNumber = std::stoll(secondNumberString);
const long long modValue = 1000000007LL;
return ((firstNumber % modValue) * (secondNumber % modValue)) % modValue;
}
};
class Solution:
def multiply_two_lists(self, firstList: 'Node', secondList: 'Node') -> int:
currentNode = firstList
firstNumberString = ""
while currentNode is not None:
digit = currentNode.data
firstNumberString += str(digit)
currentNode = currentNode.next
firstNumber = int(firstNumberString)
currentNode = secondList
secondNumberString = ""
while currentNode is not None:
digit = currentNode.data
secondNumberString += str(digit)
currentNode = currentNode.next
secondNumber = int(secondNumberString)
modValue = 1000000007
return ((firstNumber % modValue) * (secondNumber % modValue)) % modValue
Time Complexity
- Traversing the first list:
The algorithm traverses the entire first linked list to build the string representation of the number. If there are \(n_1\) nodes in the first list, this traversal takes \(O(n_1)\).
- Traversing the second list:
The algorithm traverses the entire second linked list to build the string representation of the number. If there are \(n_2\) nodes in the second list, this traversal takes \(O(n_2)\).
- Converting strings to integers:
The conversion of a string to a long long integer using
std::stoll()takes \(O(n_1)\) and \(O(n_2)\) for the first and second lists, respectively, where \(n_1\) and \(n_2\) are the lengths of the number strings. - Multiplication:
Multiplying two long long integers takes constant time, \(O(1)\).
- Overall Time Complexity:
The overall time complexity is \(O(n_1 + n_2)\), where \(n_1\) is the length of the first list and \(n_2\) is the length of the second list.
Space Complexity
- Auxiliary Space:
Space is required for storing the string representations of the numbers. If the first list has \(n_1\) digits and the second list has \(n_2\) digits, the space used by the strings is \(O(n_1 + n_2)\). Additionally, the algorithm uses constant space for storing the final result and a few variables.
- Overall Space Complexity:
The overall space complexity is \(O(n_1 + n_2)\), where \(n_1\) and \(n_2\) are the lengths of the first and second linked lists, respectively.