Given a sorted doubly linked list and an element x, you need to insert the element x into the correct position in the sorted Doubly linked list(DLL).
Note: The DLL is sorted in ascending order
Example:
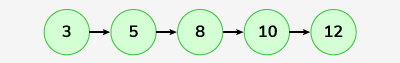
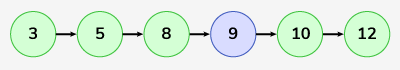
Input: LinkedList: 3->5->8->10->12 , x = 9
Output: 3->5->8->9->10->12
Explanation: Here node 9 is inserted in the Doubly Linked-List.
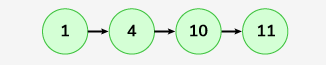
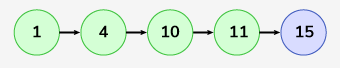
Input: LinkedList: 1->4->10->11 , x = 15
Output: 1->4->10->11->15
Constraints:
1 <= number of nodes <= 103
1 <= node -> data , x <= 104
Approach 01:
-
C++
-
Python
class Solution {
public:
Node* sortedInsert(Node* head, int value) {
Node* newNode = new Node;
newNode->data = value;
newNode->next = NULL;
newNode->prev = NULL;
if (head == NULL) {
return newNode;
}
Node* current = head;
// Insert at the beginning if the new node's value is smaller than the head's value
if (current->data >= value) {
newNode->next = head;
head->prev = newNode;
return newNode;
}
// Traverse to find the insertion point
while (current->next != NULL && current->data < value) {
current = current->next;
}
// Insert at the end if the current node's value is smaller than the new node's value
if (current->data < value) {
current->next = newNode;
newNode->prev = current;
} else {
// Insert in the middle
newNode->prev = current->prev;
newNode->next = current;
current->prev->next = newNode;
current->prev = newNode;
}
return head;
}
};
class Solution:
def sortedInsert(self, head, value):
newNode = Node(value)
if head is None:
return newNode
current = head
# Insert at the beginning if the new node's value is smaller than the head's value
if current.data >= value:
newNode.next = head
head.prev = newNode
return newNode
# Traverse to find the insertion point
while current.next is not None and current.data < value:
current = current.next
# Insert at the end if the current node's value is smaller than the new node's value
if current.data < value:
current.next = newNode
newNode.prev = current
else:
# Insert in the middle
newNode.prev = current.prev
newNode.next = current
current.prev.next = newNode
current.prev = newNode
return head
Time Complexity
- Insertion at the Beginning:
If the new node has a value smaller than the current head node’s value, insertion happens in constant time, \(O(1)\).
- Traversal to Find the Insertion Point:
In the worst case, the function may need to traverse the entire list to find the appropriate insertion point. This operation has a time complexity of \(O(n)\), where \(n\) is the number of nodes in the list.
- Insertion at the End or Middle:
Once the correct position is found, inserting the new node has a constant time complexity of \(O(1)\).
- Overall Time Complexity:
The overall time complexity is \(O(n)\), as the primary time-consuming step is traversing the list to find the correct insertion point.
Space Complexity
- Auxiliary Space for New Node:
Creating a new node requires \(O(1)\) additional space.
- Overall Space Complexity:
Since no additional data structures are used apart from the new node, the space complexity is \(O(1)\).