You are given a 0-indexed 2D integer array of events where events[i] = [startTimei, endTimei, valuei]. The ith event starts at startTimeiand ends at endTimei, and if you attend this event, you will receive a value of valuei. You can choose at most two non-overlapping events to attend such that the sum of their values is maximized.
Return this maximum sum.
Note that the start time and end time is inclusive: that is, you cannot attend two events where one of them starts and the other ends at the same time. More specifically, if you attend an event with end time t, the next event must start at or after t + 1.
Example 1:
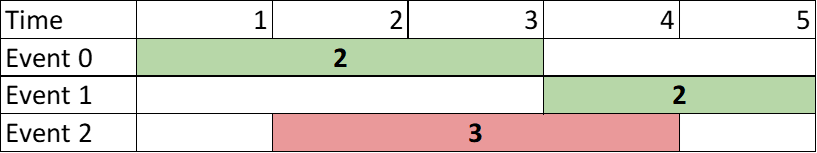
Input: events = [[1,3,2],[4,5,2],[2,4,3]] Output: 4 Explanation: Choose the green events, 0 and 1 for a sum of 2 + 2 = 4.
Example 2:
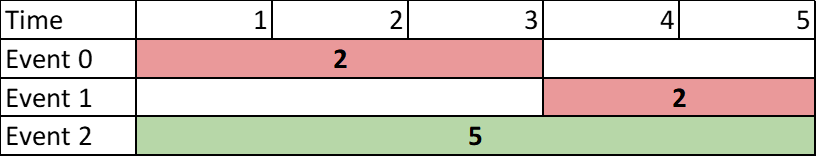
Input: events = [[1,3,2],[4,5,2],[1,5,5]] Output: 5 Explanation: Choose event 2 for a sum of 5.
Example 3:

Input: events = [[1,5,3],[1,5,1],[6,6,5]] Output: 8 Explanation: Choose events 0 and 2 for a sum of 3 + 5 = 8.
Constraints:
2 <= events.length <= 105events[i].length == 31 <= startTimei <= endTimei <= 1091 <= valuei <= 106
Approach 01:
-
C++
-
Python
class Solution {
public:
int maxTwoEvents(vector<vector<int>>& events) {
vector<tuple<int, int, int>> timeline;
for (const auto& event : events) {
int start = event[0];
int end = event[1];
int value = event[2];
timeline.emplace_back(start, 1, value); // Start of an event
timeline.emplace_back(end + 1, -1, value); // End of an event
}
sort(timeline.begin(), timeline.end()); // Sort by time
int maxEventValue = 0; // Maximum value of a single event seen so far
int maxCombinedValue = 0; // Best value of combining two events
for (const auto& [time, eventType, eventValue] : timeline) {
if (eventType == 1) { // Start of an event
maxCombinedValue = max(maxCombinedValue, maxEventValue + eventValue);
} else if (eventType == -1) { // End of an event
maxEventValue = max(maxEventValue, eventValue);
}
}
return maxCombinedValue;
}
};
class Solution:
def maxTwoEvents(self, events: List[List[int]]) -> int:
timeline = []
for start, end, value in events:
timeline.append((start, 1, value)) # Add the start of an event
timeline.append((end + 1, -1, value)) # Add the end of an event
timeline.sort() # Sort by time
maxEventValue = 0 # Maximum value of a single event seen so far
maxCombinedValue = 0 # Best value of combining two events
for time, eventType, eventValue in timeline:
if eventType == 1: # Start of an event
maxCombinedValue = max(maxCombinedValue, maxEventValue + eventValue)
elif eventType == -1: # End of an event
maxEventValue = max(maxEventValue, eventValue)
return maxCombinedValue
Time Complexity
- Building the Timeline:
- For each event, two entries are added to the timeline (start and end+1).
- Processing \(n\) events takes \(O(n)\).
- Sorting:
- The timeline is sorted based on time, which involves \(2n\) entries.
- Sorting takes \(O(2n \log(2n))\), simplified to \(O(n \log n)\).
- Traversal:
- The sorted timeline is traversed once to compute the result.
- This traversal takes \(O(2n)\), simplified to \(O(n)\).
- Overall Time Complexity:
The total time complexity is \(O(n \log n)\), dominated by the sorting step.
Space Complexity
- Timeline Storage:
- The timeline stores \(2n\) entries for \(n\) events.
- This requires \(O(2n)\), simplified to \(O(n)\) space.
- Sorting Auxiliary Space:
- Sorting the timeline requires \(O(n)\) additional space for the sorting algorithm (depending on the implementation).
- Other Variables:
- Variables like
maxEventValue,maxCombinedValue, and the loop variables require \(O(1)\) space.
- Variables like
- Overall Space Complexity:
The space complexity is \(O(n)\), dominated by the timeline storage.