Fruits are available at some positions on an infinite x-axis. You are given a 2D integer array fruits where fruits[i] = [positioni, amounti] depicts amounti fruits at the position positioni. fruits is already sorted by positioni in ascending order, and each positioni is unique.
You are also given an integer startPos and an integer k. Initially, you are at the position startPos. From any position, you can either walk to the left or right. It takes one step to move one unit on the x-axis, and you can walk at most k steps in total. For every position you reach, you harvest all the fruits at that position, and the fruits will disappear from that position.
Return the maximum total number of fruits you can harvest.
Example 1:
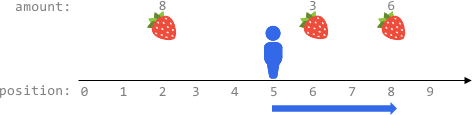
Input: fruits = [[2,8],[6,3],[8,6]], startPos = 5, k = 4 Output: 9 Explanation: The optimal way is to: - Move right to position 6 and harvest 3 fruits - Move right to position 8 and harvest 6 fruits You moved 3 steps and harvested 3 + 6 = 9 fruits in total.
Example 2:
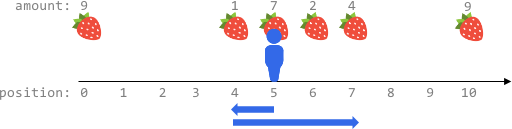
Input: fruits = [[0,9],[4,1],[5,7],[6,2],[7,4],[10,9]], startPos = 5, k = 4 Output: 14 Explanation: You can move at most k = 4 steps, so you cannot reach position 0 nor 10. The optimal way is to: - Harvest the 7 fruits at the starting position 5 - Move left to position 4 and harvest 1 fruit - Move right to position 6 and harvest 2 fruits - Move right to position 7 and harvest 4 fruits You moved 1 + 3 = 4 steps and harvested 7 + 1 + 2 + 4 = 14 fruits in total.
Example 3:
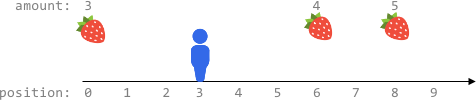
Input: fruits = [[0,3],[6,4],[8,5]], startPos = 3, k = 2 Output: 0 Explanation: You can move at most k = 2 steps and cannot reach any position with fruits.
Constraints:
1 <= fruits.length <= 105fruits[i].length == 20 <= startPos, positioni <= 2 * 105positioni-1 < positionifor anyi > 0(0-indexed)1 <= amounti <= 1040 <= k <= 2 * 105
Approach 01:
-
C++
-
Python
class Solution {
public:
int maxTotalFruits(vector<vector<int>>& fruits, int startPos, int k) {
const int furthestFruitPos = max(startPos, fruits.back()[0]);
int maxFruitsCollected = 0;
vector<int> fruitAmounts(furthestFruitPos + 1);
vector<int> prefixSum(furthestFruitPos + 2);
for (const vector<int>& fruit : fruits)
fruitAmounts[fruit[0]] = fruit[1];
partial_sum(fruitAmounts.begin(), fruitAmounts.end(),
prefixSum.begin() + 1);
auto collectFruits = [&](int leftSteps, int rightSteps) {
int leftBound = max(0, startPos - leftSteps);
int rightBound = min(furthestFruitPos, startPos + rightSteps);
return prefixSum[rightBound + 1] - prefixSum[leftBound];
};
// Move right first
int maxRightSteps = min(furthestFruitPos - startPos, k);
for (int rightSteps = 0; rightSteps <= maxRightSteps; ++rightSteps) {
int leftSteps = max(0, k - 2 * rightSteps);
maxFruitsCollected =
max(maxFruitsCollected, collectFruits(leftSteps, rightSteps));
}
// Move left first
int maxLeftSteps = min(startPos, k);
for (int leftSteps = 0; leftSteps <= maxLeftSteps; ++leftSteps) {
int rightSteps = max(0, k - 2 * leftSteps);
maxFruitsCollected =
max(maxFruitsCollected, collectFruits(leftSteps, rightSteps));
}
return maxFruitsCollected;
}
};
Time Complexity:
- Building fruitAmounts and prefixSum:Let \( n \) be the number of entries in
fruits, and \( m \) be the furthest fruit position. FillingfruitAmountstakes \(O(n)\), and computingprefixSumtakes \(O(m)\). - Loop for collecting fruits:Both loops (right-first and left-first) run at most \(O(k)\) times, and each iteration does \(O(1)\) work.
- Total Time Complexity:\(O(n + m + k)\).
Space Complexity:
fruitAmountsandprefixSum:Both use \(O(m)\) space where \( m \) is the largest fruit position.- Total Space Complexity:\(O(m)\).
class Solution:
def maxTotalFruits(self, fruits: list[list[int]], startPos: int, k: int) -> int:
furthestFruitPos = max(startPos, fruits[-1][0])
maxFruitsCollected = 0
fruitAmounts = [0] * (furthestFruitPos + 1)
prefixSum = [0] * (furthestFruitPos + 2)
for position, amount in fruits:
fruitAmounts[position] = amount
for i in range(furthestFruitPos + 1):
prefixSum[i + 1] = prefixSum[i] + fruitAmounts[i]
def collectFruits(leftSteps, rightSteps):
leftBound = max(0, startPos - leftSteps)
rightBound = min(furthestFruitPos, startPos + rightSteps)
return prefixSum[rightBound + 1] - prefixSum[leftBound]
# Move right first
maxRightSteps = min(furthestFruitPos - startPos, k)
for rightSteps in range(maxRightSteps + 1):
leftSteps = max(0, k - 2 * rightSteps)
maxFruitsCollected = max(maxFruitsCollected, collectFruits(leftSteps, rightSteps))
# Move left first
maxLeftSteps = min(startPos, k)
for leftSteps in range(maxLeftSteps + 1):
rightSteps = max(0, k - 2 * leftSteps)
maxFruitsCollected = max(maxFruitsCollected, collectFruits(leftSteps, rightSteps))
return maxFruitsCollected
Time Complexity:
- Building
fruitAmountsandprefixSum:Let \( n \) be the number of entries in
fruits, and \( m \) be the furthest fruit position. FillingfruitAmountstakes \(O(n)\), and computingprefixSumtakes \(O(m)\). - Loop for collecting fruits:
Both loops (right-first and left-first) run at most \(O(k)\) times, each doing \(O(1)\) work using prefix sum.
- Total Time Complexity:
\(O(n + m + k)\).
Space Complexity:
fruitAmountsandprefixSum:Both arrays require \(O(m)\) space, where \( m \) is the furthest fruit position.
- Total Space Complexity:
\(O(m)\).