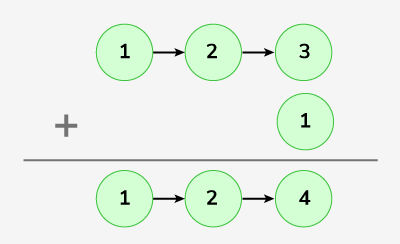
You are given a linked list where each element in the list is a node and have an integer data. You need to add 1 to the number formed by concatinating all the list node numbers together and return the head of the modified linked list.
Note: The head represents the first element of the given array.
Examples :
Input: LinkedList: 4->5->6 Output: 457
Explanation: 4->5->6 represents 456 and when 1 is added it becomes 457.
Input: LinkedList: 1->2->3 Output: 124
Explanation: 1->2->3 represents 123 and when 1 is added it becomes 124.
Expected Time Complexity: O(n)
Expected Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Constraints:
1 <= len(list) <= 105
0 <= list[i] <= 105
Approach 01:
-
C++
-
Python
class Solution {
public:
int carry = 0;
// Helper function to recursively add one to the linked list
int addOneToLinkedList(Node* currentNode) {
if (currentNode == nullptr) {
// Base case: when the end of the list is reached, initiate carry as 1
return 1;
}
// Recursive call to add one to the next node
carry = addOneToLinkedList(currentNode->next);
// Add carry to the current node's data
currentNode->data += carry;
if (currentNode->data < 10) {
// No further carry required
return 0;
}
// Carry is needed, so set current node's data to 0
currentNode->data = 0;
return 1;
}
Node* addOne(Node* head) {
carry = addOneToLinkedList(head);
if (carry) {
// If there's a carry remaining, add a new node at the beginning
Node* newNode = new Node(1);
newNode->next = head;
return newNode;
}
return head;
}
};
Time Complexity
- Recursive Traversal:
The function
addOneToLinkedListrecursively traverses each node of the linked list exactly once. Thus, the time complexity of traversing the linked list is \( O(n) \), where \( n \) is the number of nodes in the linked list. - Overall Time Complexity:
The overall time complexity is \( O(n) \) due to the single traversal of the linked list.
Space Complexity
- Recursive Call Stack:
The recursion depth is equal to the number of nodes in the linked list. Hence, the space complexity due to the recursion stack is \( O(n) \), where \( n \) is the number of nodes in the linked list.
- Auxiliary Space:
Aside from the recursive call stack, additional space used is minimal, as the modifications are done in-place.
- Overall Space Complexity:
The overall space complexity is \( O(n) \) due to the recursive call stack.
class Solution:
def addOne(self, head):
# Traverse the linked list and construct the number as a string
currentNode = head
numberString = ""
while currentNode is not None:
numberString += str(currentNode.data)
currentNode = currentNode.next
# Convert the number string to an integer, add one, and convert back to a string
incrementedNumberString = str(int(numberString) + 1)
# Create a new linked list from the incremented number string
newHead = None
lastNode = None
for digit in incrementedNumberString:
if newHead is None:
newHead = Node(int(digit))
lastNode = newHead
else:
lastNode.next = Node(int(digit))
lastNode = lastNode.next
return newHead
Time Complexity
- Linked List Traversal:
The function first traverses the entire linked list to construct a string representation of the number. This traversal takes \( O(n) \) time, where \( n \) is the number of nodes in the linked list.
- String Conversion and Increment:
Converting the number string to an integer, adding one, and converting it back to a string also takes \( O(n) \) time in the worst case, where \( n \) is the number of digits in the string representation of the number.
- Creating a New Linked List:
Constructing a new linked list from the incremented number string involves iterating through the digits of the incremented number string, which also takes \( O(n) \) time.
- Overall Time Complexity:
The overall time complexity is \( O(n) \), where \( n \) is the number of nodes in the linked list.
Space Complexity
- String Representation:
Storing the number as a string requires \( O(n) \) additional space, where \( n \) is the number of nodes in the linked list.
- New Linked List:
Creating a new linked list also requires \( O(n) \) space to store the new nodes.
- Overall Space Complexity:
The overall space complexity is \( O(n) \) due to the storage needed for the string representation of the number and the new linked list.