Given a Circular Linked List. The task is to delete the given node, key in the circular linked list, and reverse the circular linked list.
Note: You don’t have to print anything, just return head of the modified list in each function.
Examples:
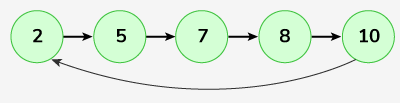
Input: Linked List: 2->5->7->8->10, key = 8
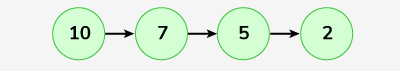
Output: 10->7->5->2
Explanation:
After deleting 8 from the given circular linked list, it has elements as 2, 5, 7, 10. Now, reversing this list will result in 10, 7, 5, 2.
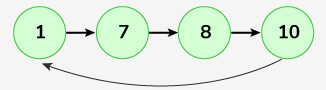
Input: Linked List: 1->7->8->10, key = 8
Output: 10->7->1Explanation:
After deleting 8 from the given circular linked list, it has elements as 1, 7,10. Now, reversing this list will result in 10, 7, 1.
Expected Time Complexity: O(n)
Expected Auxillary Space: O(1)
Constraints:
2 <= number of nodes, key <= 105
1 <= node -> data <= 105
Approach 01:
-
C++
-
Python
class Solution {
public:
// Function to reverse a circular linked list
Node* reverse(Node* head) {
Node* current = head;
Node* previous = nullptr;
Node* nextNode = nullptr;
Node* temp = nullptr;
do {
nextNode = current->next;
current->next = previous;
previous = current;
current = nextNode;
} while (current != head);
head->next = previous;
head = previous;
return head;
}
// Function to delete a node from the circular linked list
Node* deleteNode(Node* head, int key) {
Node* current = head;
Node* temp = nullptr;
// If head needs to be deleted
if (current->data == key) {
temp = head;
while (temp->next != head) {
temp = temp->next;
}
temp->next = current->next;
current = temp->next;
head = current;
return head;
}
bool found = false;
current = head;
while (current->next != head) {
if (current->next->data == key) {
found = true;
break;
}
current = current->next;
}
if (found) {
current->next = current->next->next;
return head;
} else {
return head;
}
}
};
class Solution:
# Function to reverse a circular linked list
def reverse(self, head: 'Node') -> 'Node':
current = head
previous = None
nextNode = None
while True:
nextNode = current.next
current.next = previous
previous = current
current = nextNode
if current == head:
break
head.next = previous
head = previous
return head
# Function to delete a node from the circular linked list
def deleteNode(self, head: 'Node', key: int) -> 'Node':
current = head
temp = None
# If head needs to be deleted
if current.data == key:
temp = head
while temp.next != head:
temp = temp.next
temp.next = current.next
head = temp.next
return head
found = False
current = head
while current.next != head:
if current.next.data == key:
found = True
break
current = current.next
if found:
current.next = current.next.next
return head
else:
return head
Time Complexity
reverse(Node* head):The function reverses the circular linked list by iterating through each node once. Since it traverses the entire list exactly once, the time complexity is \(O(n)\), where \(n\) is the number of nodes in the list.
deleteNode(Node* head, int key):The function finds and deletes the node with the specified key:
- If the node to delete is the head, the function traverses the list to find the last node (which takes \(O(n)\)) and updates the pointers.
- If the node to delete is not the head, the function iterates through the list to find the node to delete, which also takes \(O(n)\) in the worst case.
Therefore, the time complexity of the `deleteNode` function is \(O(n)\).
- Overall Time Complexity:
Both functions—
reverseanddeleteNode—have a time complexity of \(O(n)\), where \(n\) is the number of nodes in the circular linked list.
Space Complexity
reverse(Node* head):The function uses a few extra pointers (
current,previous,nextNode) to reverse the list. All these require constant space, so the space complexity is \(O(1)\).deleteNode(Node* head, int key):The function uses a few extra pointers (
current,temp) to traverse the list and delete the node. These variables require constant space, so the space complexity is \(O(1)\).- Overall Space Complexity:
The overall space complexity of both functions is \(O(1)\), as they do not use any additional data structures that grow with the input size.