Given a grid of size n*m (n is the number of rows and m is the number of columns in the grid) consisting of ‘W’s (Water) and ‘L’s (Land). Find the number of islands.
Note: An island is either surrounded by water or the boundary of a grid and is formed by connecting adjacent lands horizontally or vertically or diagonally i.e., in all 8 directions.
Examples:
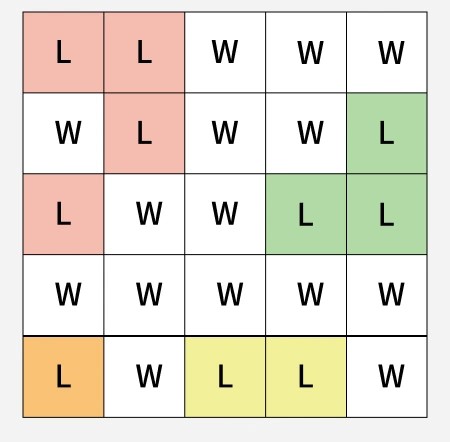
Input: grid[][] = [['L', 'L', 'W', 'W', 'W'], ['W', 'L', 'W', 'W', 'L'], ['L', 'W', 'W', 'L', 'L'], ['W', 'W', 'W', 'W', 'W'], ['L', 'W', 'L', 'L', 'W']] Output: 4 Explanation: The image below shows all the 4 islands in the grid.
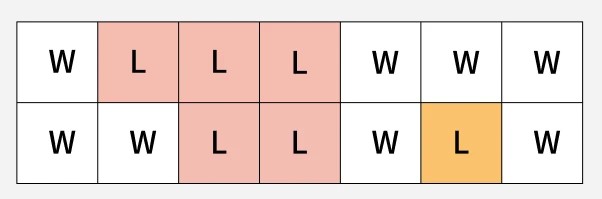
Input: grid[][] = [['W', 'L', 'L', 'L', 'W', 'W', 'W'], ['W', 'W', 'L', 'L', 'W', 'L', 'W']] Output: 2 Expanation: The image below shows 2 islands in the grid.
Constraints:
1 ≤ n, m ≤ 500
grid[i][j] = {‘L’, ‘W’}
Approach 01:
-
C++
-
Python
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
int countIslands(vector<vector<char>>& grid) {
int deltaX[8] = {0, 0, 1, -1, 1, 1, -1, -1};
int deltaY[8] = {1, -1, 0, 0, -1, 1, -1, 1};
int rows = grid.size();
int cols = grid[0].size();
int islandCount = 0;
for (int row = 0; row < rows; row++) {
for (int col = 0; col < cols; col++) {
if (grid[row][col] == 'L') {
queue<pair<int, int>> bfsQueue;
bfsQueue.push({row, col});
grid[row][col] = 'W';
islandCount++;
while (!bfsQueue.empty()) {
auto currentCell = bfsQueue.front();
bfsQueue.pop();
for (int dir = 0; dir < 8; dir++) {
int newRow = currentCell.first + deltaX[dir];
int newCol = currentCell.second + deltaY[dir];
if (newRow >= 0 && newRow < rows &&
newCol >= 0 && newCol < cols &&
grid[newRow][newCol] == 'L') {
bfsQueue.push({newRow, newCol});
grid[newRow][newCol] = 'W';
}
}
}
}
}
}
return islandCount;
}
};
from collections import deque
from typing import List
class Solution:
def numIslands(self, grid: List[List[str]]) -> int:
deltaX = [0, 0, 1, -1, 1, 1, -1, -1]
deltaY = [1, -1, 0, 0, -1, 1, -1, 1]
rows = len(grid)
cols = len(grid[0])
islandCount = 0
for row in range(rows):
for col in range(cols):
if grid[row][col] == 'L':
bfsQueue = deque()
bfsQueue.append((row, col))
grid[row][col] = 'W'
islandCount += 1
while bfsQueue:
currentRow, currentCol = bfsQueue.popleft()
for direction in range(8):
newRow = currentRow + deltaX[direction]
newCol = currentCol + deltaY[direction]
if 0 <= newRow < rows and 0 <= newCol < cols and grid[newRow][newCol] == 'L':
bfsQueue.append((newRow, newCol))
grid[newRow][newCol] = 'W'
return islandCount
Time Complexity:
- Outer Grid Traversal:
Each cell in the grid is visited once, giving a base complexity of \( O(M \times N) \), where \( M \) is the number of rows and \( N \) is the number of columns.
- BFS Traversal:
Each land cell is visited once during BFS and marked as water to avoid revisiting, so total BFS work across all islands is still \( O(M \times N) \).
- Total Time Complexity:
The overall time complexity is \( O(M \times N) \).
Space Complexity:
- BFS Queue:
In the worst case, the queue can hold all land cells, contributing up to \( O(M \times N) \) space.
- In-Place Grid Modification:
No extra visited array is used; the input grid is modified in-place.
- Total Space Complexity:
The space complexity is \( O(M \times N) \) due to the queue.