Given a binary matrix mat of size n * m, find out the maximum length of a side of a square sub-matrix with all 1s.
Examples:
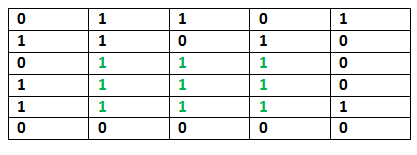
Input: n = 6, m = 5 mat = [[0, 1, 1, 0, 1], [1, 1, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 1, 1, 1, 0],
[1, 1, 1, 1, 0],
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0]] Output: 3 Explanation:
The maximum length of a side of the square sub-matrix is 3 where every element is 1.
Input: n = 2, m = 2 mat = [[1, 1], [1, 1]] Output: 2 Explanation: The maximum length of a side of the square sub-matrix is 2. The matrix itself is the maximum sized sub-matrix in this case.
Input: n = 2, m = 2 mat = [[0, 0], [0, 0]] Output: 0 Explanation: There is no 1 in the matrix.
Expected Time Complexity: O(n*m)
Expected Auxiliary Space: O(n*m)
Constraints:
1 ≤ n, m ≤ 500
0 ≤ mat[i][j] ≤ 1
Approach 01:
-
C++
-
Python
class Solution {
public:
int maxSquare(int rows, int cols, vector<vector<int>> matrix) {
int max_square_size = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < rows; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < cols; j++){
if(matrix[i][j] == 1){
if(i == 0 || j == 0)
matrix[i][j] = 1;
else{
matrix[i][j] = min({matrix[i-1][j-1], matrix[i-1][j], matrix[i][j-1]}) + 1;
}
max_square_size = max(max_square_size, matrix[i][j]);
}
}
}
return max_square_size;
}
};
from typing import List
class Solution:
def maxSquare(self, rows: int, cols: int, matrix: List[List[int]]) -> int:
max_square_size = 0
for i in range(rows):
for j in range(cols):
if matrix[i][j] == 1:
if i == 0 or j == 0:
matrix[i][j] = 1
else:
matrix[i][j] = min(matrix[i-1][j-1], matrix[i-1][j], matrix[i][j-1]) + 1
max_square_size = max(max_square_size, matrix[i][j])
return max_square_size
Time Complexity
- Nested Loops:
The algorithm uses nested loops to traverse each element of the matrix. The outer loop runs \( \text{rows} \) times and the inner loop runs \( \text{cols} \) times.
- Overall Time Complexity:
The overall time complexity is \( O(\text{rows} \times \text{cols}) \), where \( \text{rows} \) is the number of rows and \( \text{cols} \) is the number of columns in the matrix.
Space Complexity
- In-Place Modification:
The algorithm modifies the input matrix in-place to store intermediate results. No additional space proportional to the size of the input is used.
- Overall Space Complexity:
The overall space complexity is \( O(1) \), as the algorithm only uses a constant amount of extra space for variables such as
max_square_size.