You are given a rectangular matrix, and your task is to return an array while traversing the matrix in spiral form.
Examples:
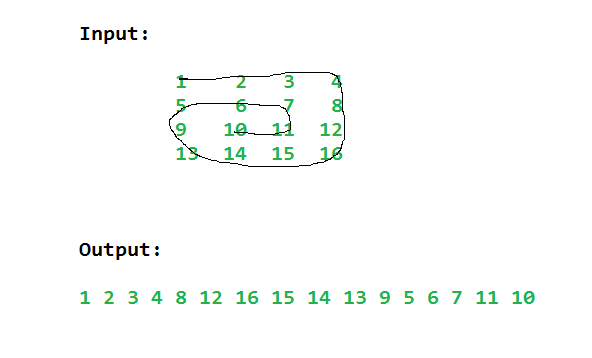
Input: matrix[][] = [[1, 2, 3, 4], [5, 6, 7, 8], [9, 10, 11, 12], [13, 14, 15,16]] Output: [1, 2, 3, 4, 8, 12, 16, 15, 14, 13, 9, 5, 6, 7, 11, 10] Explanation:
Input: matrix[][] = [[1, 2, 3, 4], [5, 6, 7, 8], [9, 10, 11, 12]] Output: [1, 2, 3, 4, 8, 12, 11, 10, 9, 5, 6, 7] Explanation: Applying same technique as shown above, output for the 2nd testcase will be 1 2 3 4 8 12 11 10 9 5 6 7.
Expected Time Complexity: O(n2)
Expected Auxiliary Space: O(n2)
Constraints:
1 <= matrix.size(), matrix[0].size() <= 100
0 <= matrix[i][j]<= 100
Approach 01:
-
C++
-
Python
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> spirallyTraverse(vector<vector<int>>& matrix) {
vector<int> result; // Vector to store the spiral order of elements
int startRow = 0; // Starting row index
int startCol = 0; // Starting column index
int endRow = matrix.size() - 1; // Ending row index
int endCol = matrix[0].size() - 1; // Ending column index
while (result.size() < matrix.size() * matrix[0].size()) {
// Traverse from left to right along the top row
for (int col = startCol; col <= endCol; ++col) {
result.push_back(matrix[startRow][col]);
}
++startRow; // Move down to the next row
if (result.size() == matrix.size() * matrix[0].size()) break;
// Traverse from top to bottom along the rightmost column
for (int row = startRow; row <= endRow; ++row) {
result.push_back(matrix[row][endCol]);
}
--endCol; // Move left to the next column
if (result.size() == matrix.size() * matrix[0].size()) break;
// Traverse from right to left along the bottom row
for (int col = endCol; col >= startCol; --col) {
result.push_back(matrix[endRow][col]);
}
--endRow; // Move up to the previous row
if (result.size() == matrix.size() * matrix[0].size()) break;
// Traverse from bottom to top along the leftmost column
for (int row = endRow; row >= startRow; --row) {
result.push_back(matrix[row][startCol]);
}
++startCol; // Move right to the next column
}
return result; // Return the spiral order of elements
}
};
from typing import List
class Solution:
def spirallyTraverse(self, matrix: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:
result = [] # List to store the spiral order of elements
startRow = 0 # Starting row index
startCol = 0 # Starting column index
endRow = len(matrix) - 1 # Ending row index
endCol = len(matrix[0]) - 1 # Ending column index
while len(result) < len(matrix) * len(matrix[0]):
# Traverse from left to right along the top row
for col in range(startCol, endCol + 1):
result.append(matrix[startRow][col])
startRow += 1 # Move down to the next row
if len(result) == len(matrix) * len(matrix[0]):
break
# Traverse from top to bottom along the rightmost column
for row in range(startRow, endRow + 1):
result.append(matrix[row][endCol])
endCol -= 1 # Move left to the next column
if len(result) == len(matrix) * len(matrix[0]):
break
# Traverse from right to left along the bottom row
for col in range(endCol, startCol - 1, -1):
result.append(matrix[endRow][col])
endRow -= 1 # Move up to the previous row
if len(result) == len(matrix) * len(matrix[0]):
break
# Traverse from bottom to top along the leftmost column
for row in range(endRow, startRow - 1, -1):
result.append(matrix[row][startCol])
startCol += 1 # Move right to the next column
return result # Return the spiral order of elements
Time Complexity
- Traversal of Matrix Elements:
The algorithm traverses each element of the matrix exactly once in spiral order. Given that there are \( m \times n \) elements in the matrix, where \( m \) is the number of rows and \( n \) is the number of columns, the time complexity is \( O(m \times n) \).
- Overall Time Complexity:
The overall time complexity of the algorithm is \( O(m \times n) \).
Space Complexity
- Result Vector:
The result vector stores all the elements of the matrix in spiral order. Therefore, the space required for the result vector is \( O(m \times n) \), where \( m \) is the number of rows and \( n \) is the number of columns.
- Auxiliary Space:
The auxiliary space used for variables like
startRow,startCol,endRow,endColis constant, i.e., \( O(1) \). - Overall Space Complexity:
The overall space complexity is \( O(m \times n) \) due to the result vector.